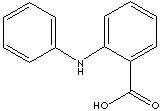
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
APPLICATIONS
Anthranilic acid, amino group substituted benzoic acid at ortho position, is used as an intermediate for production of dyes, pigments and saccharin. It has amino and carboxylic group attached in ring structure. It and its esters are used in preparing perfumes, pharmaceuticals and UV-absorber as well as corrosion inhibitors for metals and mold inhibitors in soya sauce. Fenamic Acid (N-Phenylanthranilic acid) is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals especially NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) such as Mefenamic Acid, Flufenamic acid, floctafenine, tolfenamic acid.
Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs); chemically heterogeneous large groups of drugs which suppress inflammation in a manner similar to steroids, but less side effects of sedation, respiratory depression, or addiction than steroids. They are widely used for the treatment of inflammatory disorders and painful conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, bursitis, painful menstruation, and headache. They are effective in the relief of pain and fever. NSAIDs inhibit the cyclooxygenase (COX) activity resulting in decreased synthesis of prostaglandin, leukotriene and thromboxane precursors such as the ubiquitous enzyme which catalyzes the initial step in the synthesis of prostanoids. Prostanoid is any of a group of C-20 fatty acids complex with an internal five or six carbon rings such as prostaglandins, prostanoic acid, prostacyclins, and thromboxane; derived from arachidonic acid (C-20 polyunsaturated fatty acid with four cis double bonds). The action or the synthesis of prostanoids are involved in the modulation of a variety of pathophysiologic processes including inflammation, hemostasis, thrombosis, cytoprotection, ulceration, hemodynamics and other the progression of kidney diseases. Thus, NSAIDs as non-selective inhibitors of the cyclooxygenases (both the cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 isoenzymes) may have beneficial as well as untoward effects on a variety of human diseases. Low stomach prostanoid levels caused by COX-1 inhibitors can result in ulceration and internal bleeding and perforation. The selective COX-2 inhibitors such as oxicam, meloxicam, and coxibs (celecoxib, rofecoxib, valdecoxib, parecoxib and etoricoxib) do not interfere with COX-1. The most prominent NSAID is aspirin. Nonaspirin NSAIDs can be classified based on chemical structures.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAID) by chemical structure
- Carboxylic Acid Groups
- Salicylates (Acetylsalicylate, Choline salicylate, Diflunisal, Magnesium choline salicylate, Magnesium salicylate, Salsalate)
- Acetic Acids (Bendazac, Diclofenac, Etodolac, Indomethacin, Ketorolac, Nabumetone, Sulindac, Tolmetin)
- Propionic acids (Carprofen, Fenoprofen, Flurbiprofen, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Loxoprofen, Naproxen, Naproxen sodium, Oxaprozin, Vedaprofen)
- Anthranilic acids (Meclofenamic acid, Meclofenamate sodium, Tolfenamic acid)
- Phenylacetic acids
- Aminonicotinic acids (Flunixin)
- Indole Analogs (Indomethacin, Nabumetone, Ketorolac, Etodolac,)
- Enolic Acid Groups (which doesn't have carboxylic group but acid due to the enolic hydroxy substituent)
- Pyrazolones (Phenylbutazone, Oxyphenbutazone, Dipyrone, Ramifenazone)
- Oxicams (Meloxicam, Piroxicam, Tenoxicam)
- Coxibs
- Celecoxib, Rofecoxib, Valdecoxib, Parecoxib, Etoricoxib
- Gold Salts
- Auranofin, Gold sodium thiomalate, Aurothioglucose
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
25kgs in fiber drum